 Is Blockchain Technology Environmentally Friendly? 7/7/2022 - READ MORE
Is Blockchain Technology Environmentally Friendly? 7/7/2022 - READ MOREEnvironmental concerns


Not All Crypto Currencies Are Created Equal
The underlying reason for the high energy usage, according to experts, is the process known as “Proof of Work,” which requires miners to create the cryptocurrency while receiving coins. If left unaltered, this carbon-intensive procedure may jeopardize the widespread adoption of this revolutionary technology in the long run.
New kinds of algorithms, on the other hand, are developing that may offer a foundation for more long-term working methods. One of these is ‘Proof of Stake,’ which verifies transactions based on how many coins a network member has rather than their computer processing capacity. There are efforts to decrease the mining industry’s dependence on fossil fuels, in addition to the move away from the computational power-intensive Proof of Work method.
Green Reputation And Investment
If cryptocurrencies are to thrive in the long run and continue to provide the advantages of accessibility, security, and transparency, it will be necessary to include sustainability into their ethos and design. Sustainability is also gaining traction as a platform for cryptocurrencies to develop new and distinctive value propositions that set them apart in the market. For instance, the Eco Coin is backed by ecological assets, with each ECO Coin representing one tree. This currency allows businesses to incentivize, monitor, and reward environmentally responsible employee behavior that helps them achieve their overall sustainability objectives. Governments across the globe are enacting stronger climate change legislation, and ESG investment is pushing change in many sectors, including finance. Although cryptocurrencies are still a new and unpredictable market, their environmental credentials will be scrutinized more closely. This shift is providing businesses with new possibilities to strengthen their brand reputations via sustainable initiatives, as well as a strong new source of distinction.
 What Is Web 3.0? And How Can It Transform Your Business? 12/7/2022 - READ MORE
What Is Web 3.0? And How Can It Transform Your Business? 12/7/2022 - READ MOREEvolution of the internet


Why is Web 3.0 important for businesses?
The world is moving towards a future where there will be no borders, we will all be connected, and everything will be virtual. This is what Web 3.0 is all about.
Web 1.0 was all about introducing personal computers and the Internet. Web 2.0 was the era of social media and social networking websites but Web 3.0 is the next phase of the Internet, where it becomes an entire universe of its own. Web 3.0 is the era of blockchain technology and decentralized applications. This is when we will see the rise of blockchain-based platforms that can decentralize pretty much every aspect of our lives.
Can Web 3.0 change our lives?
The Internet has changed the world for the better in many ways. Web 3.0 is the next step in the evolution of the Internet, and it will ensure that we are always able to take advantage of its benefits and avoid its frustrations. It will allow businesses to streamline their operations by cutting out the middleman and directly connecting computers. This will facilitate communication and collaboration between employees, partners, and customers, making for a more efficient business.
At Codora, we have a team of highly trained developers and designers who can provide Web 3.0 Development to businesses that want to change the world and leverage the potential benefits of blockchain. So if you’re looking for Web 3.0 development, please reach out to us.
 What is DeFi and Why does it Matter? DeFi is available 24/7 11/1/2023 - READ MORE
What is DeFi and Why does it Matter? DeFi is available 24/7 11/1/2023 - READ MOREThis question often sparks debate and backlash around what real use cases blockchain technologies have. While many ideas are being explored, one of the most promising are blockchain-based financial applications, broadly referred to as Decentralized Finance (DeFi). If you’re not familiar with DeFi yet, it’s worth paying attention. It’s been working for years and is solving genuine pain points of individuals and businesses globally. Also, by making sense of DeFi, you’ll better understand the potential applications of blockchain technologies more broadly.

DeFi 101
Traditionally, we rely on centralized entities like banks to fulfill our basic financial needs. We trust them to protect our savings, provide us with loans and facilitate day-to-day payments. It’s hard to imagine a world without them, but that’s exactly what DeFi promises.
This vision — of banking without the banks — is made possible by smart contracts, which are computer programs stored on the blockchain that automatically run when certain conditions are met.
By leveraging smart contracts and blockchain infrastructure, DeFi has a number of advantages over traditional financial institutions. It’s:
global and permissionless: users are no longer limited to local banking services, but can instead access DeFi apps from anywhere in the world
trustless: since smart contracts automatically execute, human intervention isn’t required, meaning you don’t need to rely on, or trust, third parties
always-on: DeFi is available 24/7, and isn’t limited by opening hours
transparent: the code of DeFi apps, as well as data on their usage, is publicly auditable
You might still wonder why any of that matters when the financial services you use daily are for the most part, fine. It’s important to understand that there are many different participants within the global financial system, each with unique contexts and needs. Some may be similar to you, while others face entirely different circumstances
Why is DeFi valuable?
To help you understand the value of DeFi, we’ll explore how DeFi applications benefit users including:
- unbanked individuals
- financially savvy individuals
- individuals, businesses, or nonprofits transacting globally

1) Unbanked individuals
Many of us take for granted the fact that we have bank accounts and can access basic financial services. Unfortunately, approximately 1.7 billion people are unbanked, due to factors such as geographical limitations, distrust in financial institutions, or the inability to meet minimum requirements. In fact, there may be little to no economic incentives for banks to cater to these potential customers.
However, the World Economic Forum estimates that 1.1 billion have access to a mobile phone. This presents a large opportunity for DeFi to connect the unbanked to decentralized financial services. Unlike traditional institutions, DeFi is able to scale financial services products to anyone around the world with minimal costs. For example, DeFi applications like AAVE or Compound would allow the unbanked to earn interest on their savings or even borrow money.
2) Financially savvy individuals
On the other end of the spectrum are individuals who are savvy enough to be saving and investing, and who might even have a mortgage or investment properties. They’re already in a great position, but DeFi could make things even better.
As with any other industry, a major benefit of automation is lower costs. Think about how much it costs your bank to employ their staff, use office buildings or operate physical branches. Since smart contracts can cut out intermediaries like banks, this means DeFi applications are more cost-efficient. These savings are passed onto individuals who use DeFi applications, through higher interest rates on savings — again, using applications like AAVE or Compound. For example, for every additional 1%, you earn on a balance of $10,000 is an extra $100 saved per year.
What’s more exciting is that the open and transparent nature of smart contract code means code and DeFi applications are composable. In other words, they’re like digital LEGO blocks which can be combined in unique ways. For example, Yearn is a DeFi application which automatically reinvests your savings to optimize your earnings. If AAVE has better rates than Compound, it’ll direct your funds there. In contrast, if you wanted to do the same with your traditional savings, you’d be manually setting up new accounts and transferring money between those accounts.
3) Individuals, businesses, or non-profits transacting globally
In our increasingly globalized and digital economy, individuals and businesses both have growing needs to make and accept payments in foreign currencies. For example, when individuals are shopping online for international goods, or when businesses pay salaries to global staff. The problem today isn’t that we can’t facilitate international payments — but it is expensive and often slow.
Blockchains naturally alleviate this problem since crypto tokens can be transferred globally and instantly. However, while the value of most crypto assets fluctuates wildly, it’d make the most sense to transact and store wealth in stable currencies. DeFi’s answer to this is stablecoins like USD Coin (USDC), Tether (USDT), and Dai, which are designed to maintain a stable price. You can think of these stablecoins as a digital-only form of cash, which lets you leverage the benefits of crypto infrastructure.
Using stablecoins, users can pay anyone around the world, at any time, without paying high fees or waiting for banks to open. On the other side of the transaction, businesses can receive payments instantly without high international transaction fees. Similarly, nonprofits can use applications like Endaoment to fundraise from global donors quickly. More importantly, the open data of blockchains means the movement of funds by nonprofits is more transparent and can be more closely scrutinized.
What are the risks of DeFi?
Despite these benefits, there are risks you need to be aware of when using DeFi applications. This includes:
1. Smart contract risk: since smart contracts are created from computer code, they can be prone to hacks. In 2022 alone, hackers have stolen over $3 billion of assets, with DeFi being the primary target; and
2. A lack of consumer protection: if you lose your funds due to a hack or a scam while using DeFi, no one is obliged to help or reimburse you because as we know, DeFi removes intermediaries who would typically provide that support
On the plus side, the openness of blockchain code means that with every vulnerability that’s exploited and fixed, the DeFi industry becomes safer overall. Everyone can learn from everyone else’s mistakes and experiences, which is unlike the siloed nature of traditional financial institutions.
Currently, there’s still friction around the experience of using DeFi, but as with any new technology, user experience problems will be solved. Companies like Coinbase, Argent, and Minke are already working to abstract away that complexity into slick mobile apps. In time, there’s a chance DeFi will fundamentally change how we all engage with financial services. As blockchains achieve greater scalability, it’s possible we’ll see a blockchain-based payment network operating at the scale of Visa and MasterCard. For the benefits that DeFi can, and already brings, it’s a no-brainer to try to make it work.
“A blog by Atlas DEX and Codora ApS”
 What are Smart Contracts? | How they power the DeFi Ecosystem 11/1/2023 - READ MORE
What are Smart Contracts? | How they power the DeFi Ecosystem 11/1/2023 - READ MOREWhat are Smart Contracts? | How they power the DeFi Ecosystem


So what exactly are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are code or computer programs stored on blockchains which automatically run when certain conditions are met. Despite the name, they’re not really “smart” — they can only do exactly as they’re programmed.
You can think of smart contracts as digital agreements. However, they have unique properties which distinguish them from ordinary contracts or agreements. For example, they’re:
trustless — once conditions that have been agreed upon are met, smart contracts will automatically execute. They don’t require human intervention, which means you don’t need to rely on or trust third parties to fulfil the agreement
immutable — mart contract code can’t be changed or manipulated once it’s been published to the blockchain, and
transparent — the code and details of the agreement are publicly accessible
When paired with user-friendly interfaces, smart contracts can be used to create decentralized applications (dApps). Here’s an overview of some of the dApps available on Ethereum.
Crowdfunding
Kickstarter is a crowdfunding platform which allows creators to fundraise for creative projects. It uses an all-or-nothing model, meaning creators only receive funding if their fundraising goal is met by a certain deadline. If you were to support a project, you would have to trust Kickstarter to hold your funds until that deadline, and then either return it to you, or distribute it to the creator.
However, with smart contracts, you don’t need to trust third parties like Kickstarter. For example, PartyBid is a dApp which enables crowdfunded purchases of digital assets, using a similar all-or-nothing model. Its smart contract holds the funds and depending on the outcome, it’s programmed to either let users claim tokens representing their ownership of the successfully purchased asset or re-claim their funds.
Peer-to-peer marketplaces
Another area where trust can be eliminated is in peer-to-peer marketplaces. Think about the experience of buying or selling electronic event tickets using platforms like Facebook Marketplace. As a buyer, if you make payment first, will you receive a legitimate ticket? Has it been sold to anyone else? Or as a seller, if you send the ticket first, will you receive payment? Without knowing the other party, we have to rely on signals like the quality of their personal profile.
Smart contracts remove that uncertainty. For example, OpenSea is a dApp which enables the buying and selling of digital assets. Instead of needing to vet the other party to your transaction, OpenSea’s smart contracts will automatically facilitate the correct exchange of digital assets and funds for you.
Loans
Banks are another example of an intermediary which can be cut out using smart contracts. Very simply, banks collect deposits and use those deposits to fund loans. When you ask your bank for a loan to buy property, they’ll do extensive checks to make sure you can repay it based on your personal circumstances. As part of the agreement, the bank will hold your property as collateral so that they can sell it if you fail to repay the loan.
As an alternative, decentralized financial (DeFi) applications such as AAVE have made it possible to get loans without talking to anyone. All you need to do is deposit funds as collateral into the AAVE smart contract and then choose what, and how much, you want to borrow. Unless you’re engaging in financial crimes, AAVE doesn’t even care who you are or where you’re from, and unlike your bank, it’s accessible 24/7. With smart contracts, there’s an opportunity to enable access to cheaper, trustworthy and more transparent financial services for anyone across the globe.
The future of smart contracts
Clearly, not everything needs or can be programmed into a smart contract. However, where the rules of an agreement can be clearly defined and set in stone, smart contracts can be incredibly beneficial and efficient.
What makes them even more exciting is that smart contract code is open and transparent. This turns them into digital LEGO blocks which are composable, meaning they can be freely combined in different ways. For example, Atlas DEX leverages other smart contracts to aggregate the best prices for token swaps and enable swaps to occur between blockchains.
Together, the flexibility and composability of smart contracts is enabling faster development of blockchain-based applications. While it’s impossible to know what will eventually be created, we can be sure that innovation is happening at a much faster pace!
 What are Blockchains? 26/4/2023 - READ MORE
What are Blockchains? 26/4/2023 - READ MOREBlockchain explained in 7 minutes
Maybe you’ve wondered at some point, “What even is blockchain?”


So what are blockchains?
A blockchain is a decentralized ledger — a digital record of transactions amongst a network of people. Think of a shared diary amongst a group of people, where what happens between them is recorded each day. Once an event has been recorded and accepted by everyone in the group, it becomes difficult to change as more items are recorded.
Blockchain allows for an unlimited number of anonymous parties to store information privately and securely, using software algorithms instead of a central authority. As the name suggests — Blocks are what store groups of data e.g. transactions. A series of blocks together form a Chain, which is distributed amongst the network.
So is blockchain the same as crypto?
There’s a common misconception that blockchains are a cryptocurrency — however the blockchain is the technology that supports it. Cryptocurrency is created and stored electronically in blockchains, using encryption techniques to control the creation of monetary value, and verification of the transfer of funds. For instance, some cryptocurrencies you may have heard of such as Bitcoin, Ethereum or Dogecoin, all run on their own separate blockchains.
Let’s go through step by step how a transaction is facilitated and recorded on the blockchain:
- A member of the network submits a transaction.
- The requested transaction is shared with the peer-to-peer network of computers (known as nodes).
- Validation of the transaction occurs through the network of nodes, using known algorithms, to confirm the status of the transaction.
- A verified transaction can involve the use of cryptocurrency, records, smart contracts, and other information.
- The transaction is verified and combined with other transactions to form a Block using hashing.
- The Block is added to the existing blockchain in a way that is unable to be altered or tampered with.
So what’s so revolutionary about blockchain?
There are several key benefits of blockchain, which make the technology and the products built on it unique to other types of digital databases. For example, blockchain is:
-
- tokenised — the value of an asset is tokenised and stored on the blockchain. With no physical form and existing only on the network, it is difficult to create counterfeit goods, funds or double-processing of transactions.
- decentralised — blockchain enables a peer-to-peer network that is not controlled by a central bank or authority, enabling greater security and privacy. Information sharing is not controlled by one key person or organisation.
- immutable and unalterable — transactions and records cannot be reversed, or tampered with.
This is vastly different to traditional finance and as such, provides a few core benefits. For example, there’s improved:
- privacy and identity verification — identity is typically a key target for fraud in traditional finance, and blockchain technology ensures identifying a participant of the network is traceable and verifiable at rapid speed. Rules and permissions implemented on the blockchain can manage participants in the network and their role.
- security — a malicious attack on a bank would require targeting a centralised network or server. However, with blockchain technology, each node in a peer-to-peer network acts like its own server. It’s much more difficult to compromise a network as it can verify transactions against other nodes. As such, information about your identity, funds and transactions cannot be easily obtained.
So will blockchain revolutionise my life?
You may have come across stories like Bitcoin consuming more energy than Norway or that some governments are so sceptical of cryptocurrency that they’ve made it illegal. So why do we keep using and investing in tech that causes so much controversy?
There are industries and use cases where it’s beneficial to use decentralised networks, for example:
Transparency in supply chains
Industries such as fashion, luxury goods, and pharmaceuticals have had years of issues with tracking products, creating transparency and building trust in authentic products. Research and applications of blockchain have helped with verifying authenticity, provenance and traceability. This includes reducing the amount of information flow between multiple parties when dealing with inventory, financials, and information, which could also reduce the need for lengthy human auditing. These can translate to commercial and sustainable benefits, for example knowing you’ve purchased the real deal in the luxury goods sector, or traceability of pharmaceuticals to remove counterfeit drugs, which cause a million deaths a year.
Casting your vote digitally
You may have at some point Googled ‘when will we know the result of the US election’ and waited with bated breath as votes were counted and recounted. There’s been a recent push to move voting to digital systems, particularly using blockchain and facial recognition systems. It’s still early days, with many wary of the technical risks and vulnerabilities of on-chain voting, and the challenge of explaining to the general public what blockchain is (it’s taken us a few hundred words just to cover the basics!).
Creating social good
More use cases are emerging where not-for-profit organisations are using blockchain technology to ensure funds can be donated and used in more transparent ways. There have also been more examples of people supporting causes using cryptocurrencies — The Giving Block is one start-up gaining momentum.
Blockchain has the potential to create radical change for commercial, sustainable, and social good.. Whilst it requires considerable commitment of resources, innovation and transformation, blockchain has proven to be a powerful tool in many industries. Maybe we’ll all be ‘on-chain’ one day and getting married with NFT rings, but until then keep learning through more Codora blogs.
A blog by Codora and Atlas DEX.
 What is DAO in Blockchain? 1/7/2024 - READ MORE
What is DAO in Blockchain? 1/7/2024 - READ MOREBlockchain technology has given rise to a new decentralized organizational model known as Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). A DAO is a community-led entity with no central authority, where decisions are democratically made through a transparent, blockchain-based voting process. These innovative structures have the potential to disrupt traditional hierarchical organizations and usher in a new era of decentralized, collaborative decision-making.
The concept of DAOs gained prominence around 2016 with the advent of smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum. Smart contracts enabled the autonomous execution of agreements and the formation of self-governing communities, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of decentralized organizational frameworks.
-
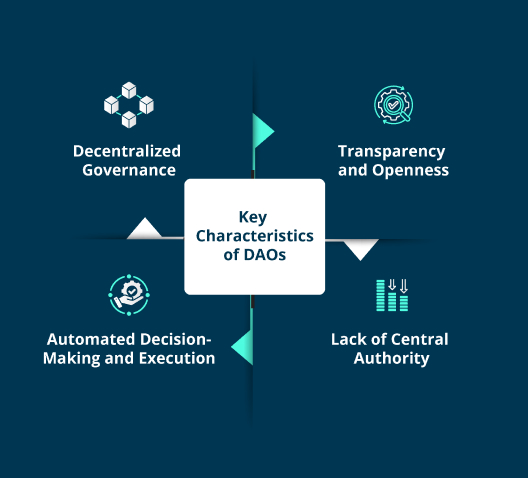
1. Decentralized Governance
DAOs are managed and governed in a decentralized manner, with members collectively making decisions through a transparent, blockchain-based voting process.
-
2. Transparency and Openness
All transactions, proposals, and decisions within a DAO are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
-
3. Automated Decision-Making and Execution
Smart contracts enforce predefined rules and execute actions automatically. They codify the processes for the DAO’s operations, enabling automated decision-making and the execution of agreed-upon actions.
-
4. Lack of Central Authority
Unlike traditional organizations, DAOs have no centralized management or leadership. Instead, they are self-governing entities, with members collectively responsible for the DAO’s direction and operations.
At the heart of a DAO are its smart contracts, which define the organization’s rules, decision-making processes, and resource management. Members of a DAO typically hold governance tokens, which grant them voting rights and the ability to participate in the decision-making process.
The DAO’s operations are funded through a shared treasury, which is managed and allocated through the DAO’s governance mechanisms. Members can submit proposals, debate, and vote on how the DAO’s resources should be used, ensuring a democratic and transparent decision-making process.
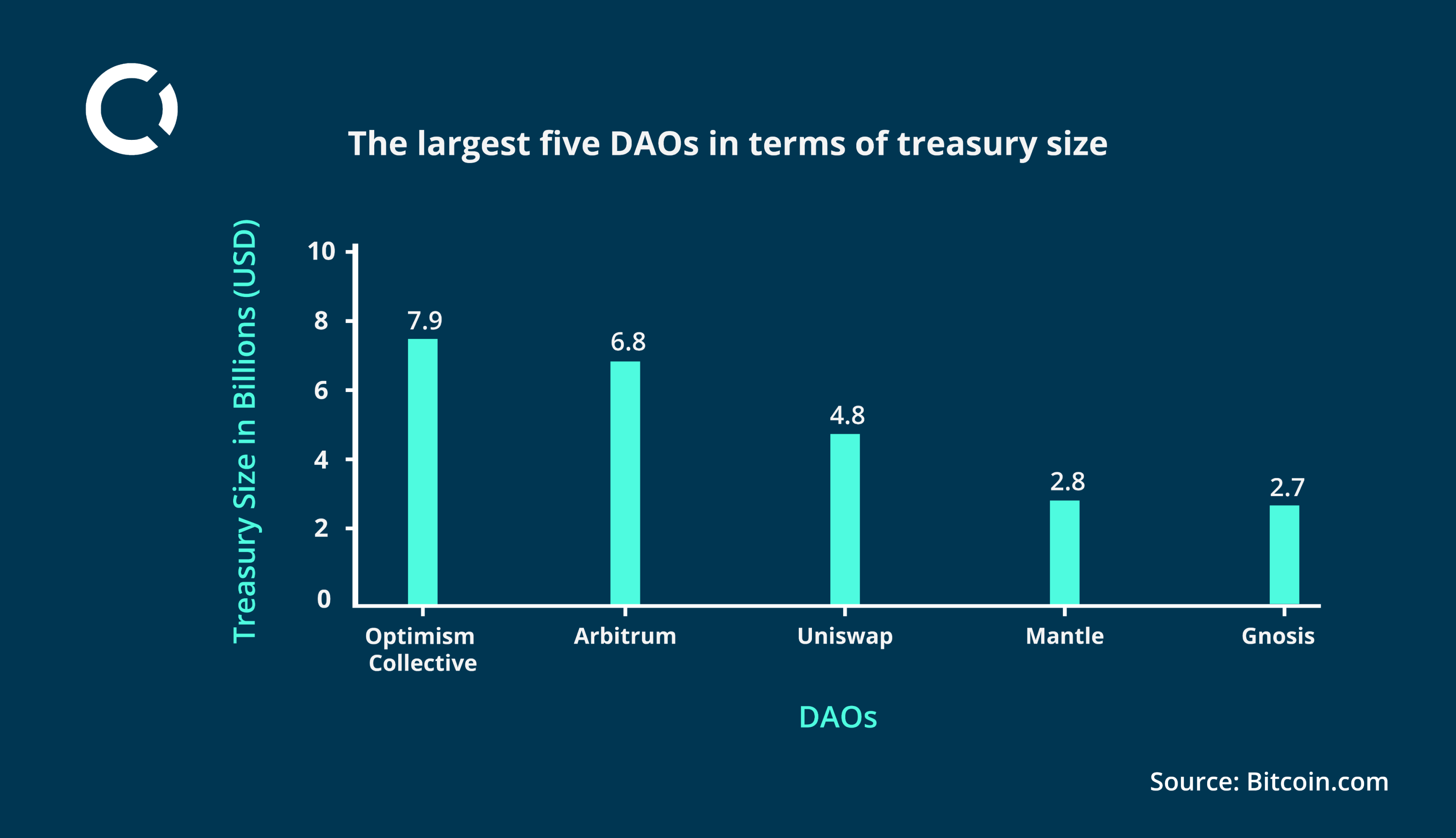
The DAO market has experienced rapid growth, with total treasuries increasing by over $20 billion since November 1, 2023, now totalling $40.1 billion. During this period, the number of DAOs holding treasuries exceeding $1 million has grown from 179 to 211.
The largest DAO in terms of treasury size is the Optimism Collective, commanding around $7.9 billion in value, followed by Arbitrum’s DAO with $6.8 billion, Uniswap’s DAO with $4.8 billion, Mantle’s DAO with $2.8 billion (previously holding the third spot), and Gnosis with $2.7 billion.
Together, the top five DAO treasuries account for $25 billion, representing 62.34% of the total $40.1 billion DAO market.
Other notable DAOs like ENS DAO and the Graph DAO manage assets ranging from $1 billion to $1.6 billion (Source: Bitcoin.com).
This substantial growth in DAO treasuries and the increasing number of million-dollar-plus DAOs underscore the rapid adoption and maturation of decentralized autonomous organizations. As technology and governance models continue to evolve, we anticipate further innovation and the emergence of new DAO frameworks in the future.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have proven to be versatile and find applications across diverse domains:
The versatility of DAOs across these use cases demonstrates their potential to revolutionize organizational governance and operational frameworks. As technology continues to advance and governance models evolve, we can expect to see further innovation in the application of DAOs across various industries and sectors.
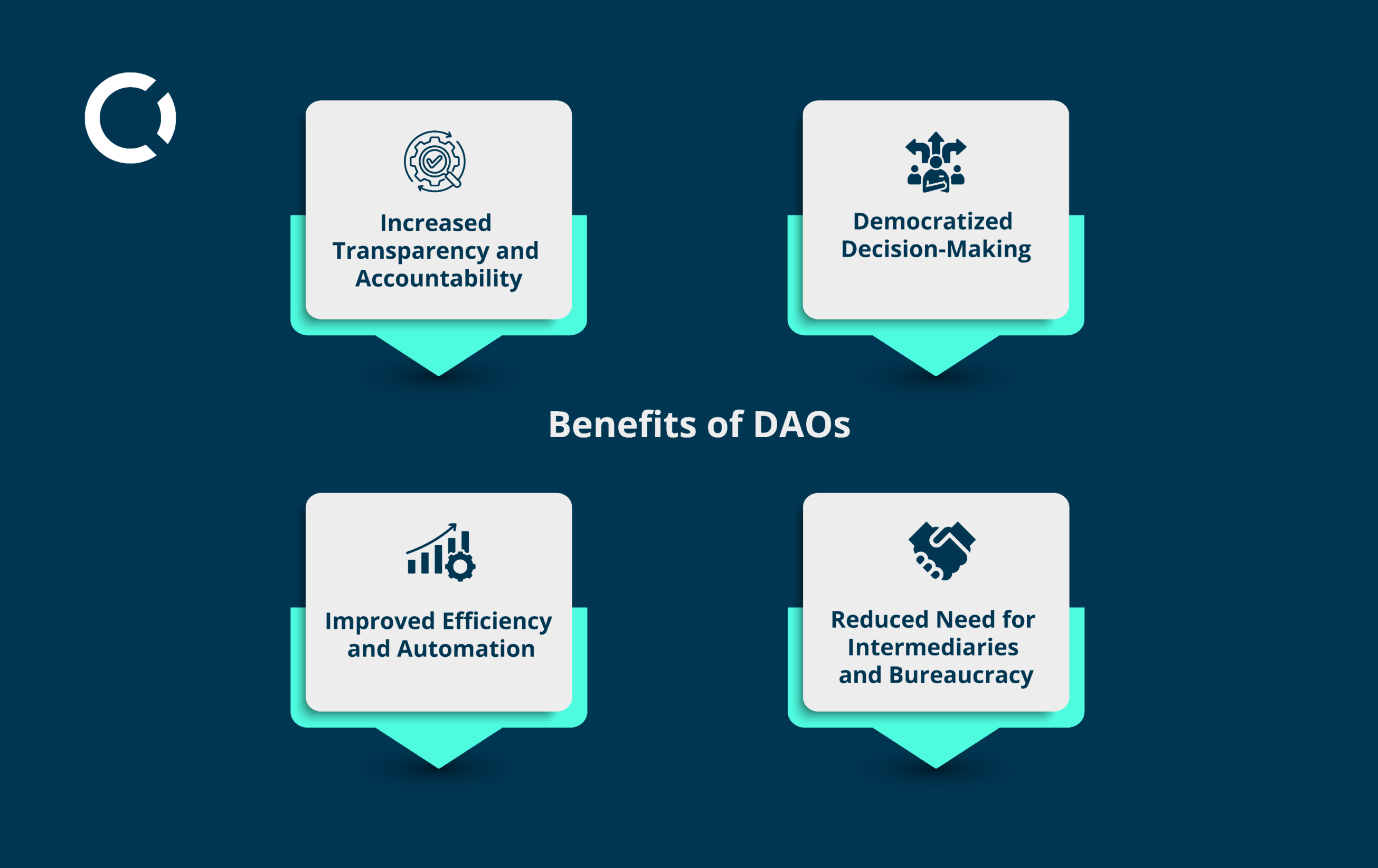
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer several advantages:
Despite their benefits, DAOs face several challenges:
These challenges underscore the need for continuous innovation, research, and collaboration within the DAO community. Addressing these issues will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of decentralized autonomous organizations.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a groundbreaking evolution in organizational frameworks, leveraging blockchain technology to enable transparent, democratic decision-making on a global scale. Their rapid adoption across sectors, from DeFi to social impact, underscores their potential to redefine governance. However, challenges such as governance complexity and regulatory uncertainties call for ongoing innovation. As DAO frameworks evolve, they promise continued advancements, shaping a decentralized future.
Join Codora at the forefront of blockchain innovation. We specialize in pioneering blockchain solutions that drive real-world impact and transformation. Whether you’re exploring DAO implementation, blockchain integration, or navigating decentralized landscapes, Codora is your trusted partner. Connect with us today at hello@codora.io to discover how we can empower your organization with decentralized autonomy, unlock efficiencies, and thrive in the digital era. Let’s shape the future of decentralized innovation together.
 The Economic Implications of Web3 on Cryptocurrencies 8/10/2024 - READ MORE
The Economic Implications of Web3 on Cryptocurrencies 8/10/2024 - READ MORETable of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
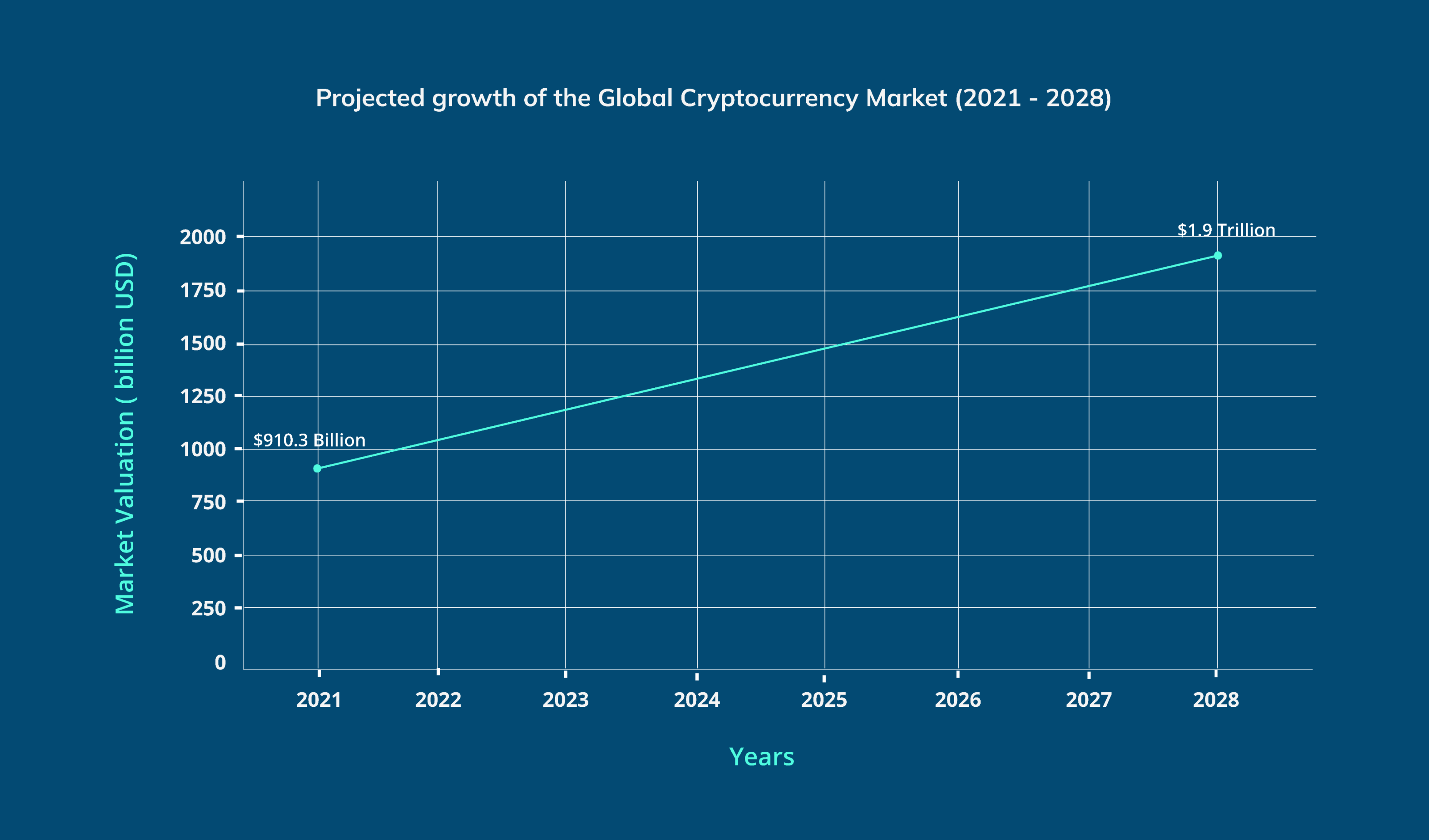
As we stand on the brink of the next internet evolution, the impact of Web3 on cryptocurrencies offers more than just technological innovation—it promises a financial metamorphosis where cryptocurrencies play a pivotal role. The global cryptocurrency market was valued at $910.3 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow to $1.9 trillion by 2028, according to Fortune Business Insights. This rapid growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of Web3 technologies, which are revolutionizing how we interact with financial systems, digital assets, and decentralized services.
In this blog, we’ll explore the economic impact of Web3 on cryptocurrencies, analyzing how this transformative technology is reshaping the global financial landscape, enabling new opportunities for innovation, inclusion, and economic growth.

2. Understanding Web3
Web3 represents the next stage in the development of the internet, not merely as an upgrade but as a revolutionary framework that redefines how users interact with digital services and conduct economic exchange. Built on blockchain technology, Web3 is characterized by decentralization, trustless protocols, and user ownership of data.
Unlike Web1.0 (read-only) and Web2.0 (interactive but centralized), Web3.0 enables peer-to-peer interactions and direct control over digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies and NFTs. Blockchain-based applications allow users to engage without intermediaries, transforming how financial transactions, data privacy, and value exchange operate in a decentralized environment.
3. The Current State of Cryptocurrencies
4. A Diverse Ecosystem
-
4.1 Ethereum
Ethereum is particularly significant, as it introduced the concept of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovation has enabled developers to build complex decentralized applications (dApps) on its platform, spanning various sectors from finance to gaming. For example, platforms like OpenSea have revolutionized the digital art market through non-fungible tokens (NFTs), allowing creators to tokenize their work and monetize it directly.
-
4.2 Solana
Solana, known for its high throughput and low transaction costs, has emerged as a strong competitor to Ethereum, attracting developers looking for scalability. Its unique consensus mechanism, Proof of History (PoH), allows for faster transaction processing, making it ideal for high-frequency applications such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and gaming platforms.
-
4.3 Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance Coin (BNB), initially created as a utility token for the Binance exchange, has evolved into a versatile asset used for trading fee discounts, transaction fees on Binance Smart Chain, and participating in token sales on the Binance Launchpad. Its growth illustrates how cryptocurrencies can adapt and serve multiple purposes within their ecosystems.
5. Institutional Adoption
The cryptocurrency market is not just a playground for retail investors; institutional interest has surged in recent years. Major companies like Tesla and MicroStrategy have publicly embraced Bitcoin (Decrypt, 2024), incorporating it into their corporate treasury strategies as a hedge against inflation and a means of diversifying their asset base. This shift has not only legitimized cryptocurrencies in the eyes of traditional investors but has also paved the way for other institutions to follow suit.
In addition to direct investments, financial institutions are developing cryptocurrency-related products. For example, Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley have begun offering clients access to Bitcoin funds (Financial Advisor IQ, 2021), while Fidelity has launched cryptocurrency trading for its institutional clients (Reuters, 2018). This institutional adoption signals a growing recognition of cryptocurrencies as a viable asset class.
The diverse functionalities and use cases of these cryptocurrencies set the stage for Web3.0’s profound economic impact, which is reshaping accessibility, business models, and financial systems.
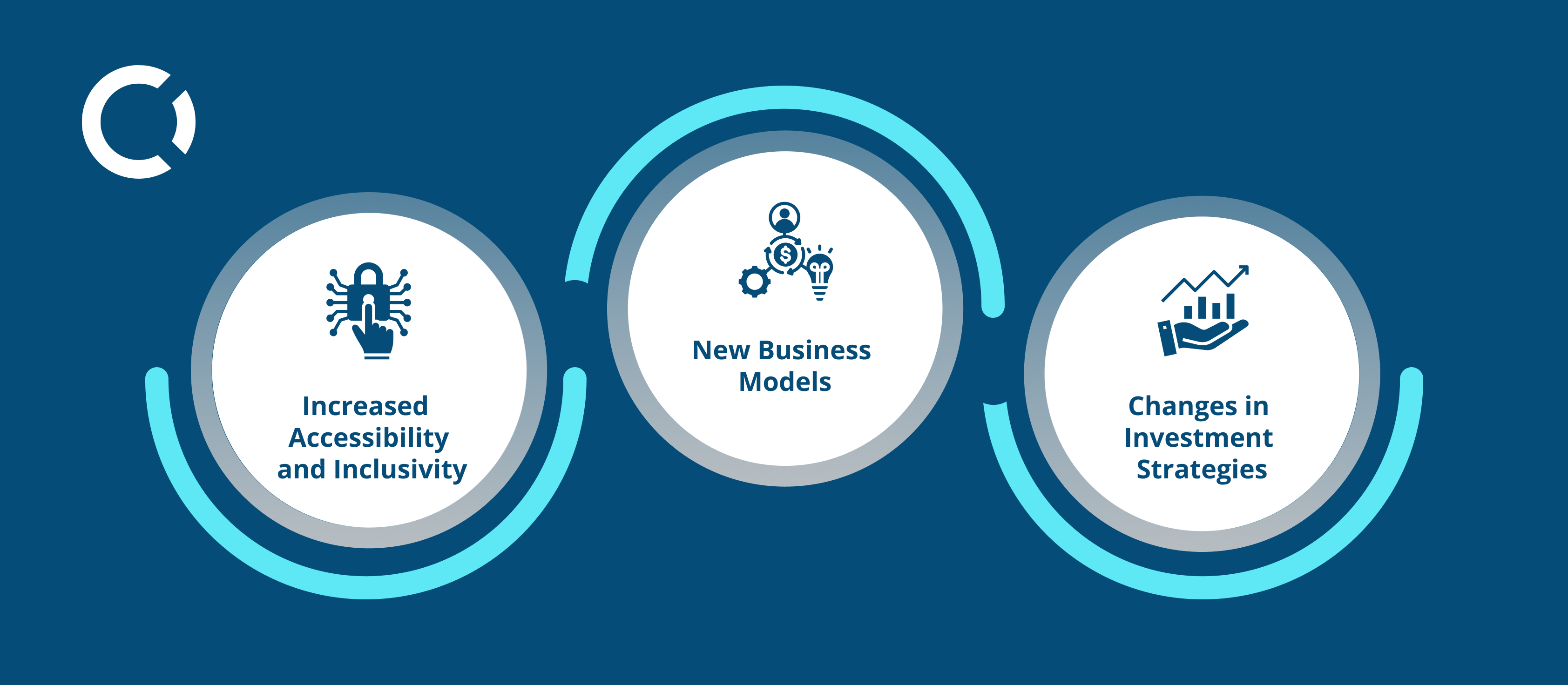
6. The Impact of Web3 on Cryptocurrencies and Its Economic Implications
-
6.1 Increased Accessibility and Inclusivity
Web3 has the potential to revolutionize financial inclusivity by democratizing access to services traditionally controlled by centralized institutions. Cryptocurrencies, when paired with blockchain technology, empower individuals—particularly those in underserved regions—to engage with global financial systems without the barriers imposed by traditional banking infrastructure.
For instance, blockchain-enabled platforms like Celo are making significant strides in providing accessible financial services to unbanked populations, especially in regions like Sub-Saharan Africa. By leveraging mobile technology, Celo allows individuals to send, receive, and store value securely, all without needing a traditional bank account. This capability is transformative in areas where banking services are limited or non-existent, enabling users to participate in the global economy through simple mobile applications.
Moreover, the use of cryptocurrencies in remittances exemplifies this increased accessibility. Traditional remittance services often charge exorbitant fees, making it difficult for families to send money across borders. Cryptocurrencies can facilitate instantaneous, low-cost transfers, empowering families to send funds home without the burden of high fees and long wait times. This not only enhances financial inclusivity but also contributes to the economic stability of communities reliant on remittances.
-
6.2 New Business Models
The advent of decentralized finance (DeFi) and tokenization is fundamentally transforming how assets are traded and managed, giving rise to innovative business models that challenge traditional financial systems. DeFi platforms enable users to lend, borrow, and earn interest without the need for intermediaries, creating a more open and efficient financial ecosystem.
For example, platforms like Uniswap have revolutionized token trading by allowing users to swap tokens directly in decentralized marketplaces. This eliminates the need for centralized exchanges, which can be vulnerable to hacks and regulatory scrutiny. By providing liquidity pools, Uniswap empowers users to participate in trading without the risks associated with centralization. The automated nature of these platforms reduces costs and increases transaction speed, further enhancing user experience.
Tokenization is another critical development reshaping investment opportunities. By representing real-world assets—such as real estate, art, and commodities—as digital tokens on a blockchain, tokenization allows for fractional ownership. This innovation democratizes access to investments that were previously limited to wealthy individuals or institutional investors.
Platforms like Securitize facilitate this process, enabling retail investors to purchase fractions of high-value assets, thereby improving liquidity across markets. For instance, a piece of real estate can be tokenized and sold in fractions, allowing multiple investors to own shares of the property. This not only opens up new avenues for investment but also enhances market efficiency by enabling easier buying and selling of assets that were traditionally illiquid.
-
6.3 Enhanced Security and Transparency
Web3 introduces enhanced security and transparency into financial transactions. The immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures that all transactions are recorded transparently and cannot be altered retroactively. This feature is particularly important in combating fraud and building trust among users.
Decentralized identity solutions, such as those provided by projects like SelfKey, further enhance security by allowing individuals to control their personal data. Users can verify their identities without exposing sensitive information, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. This level of security is crucial in attracting more people to engage in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, especially those who may have been hesitant due to safety concerns.
As security and transparency become increasingly integral to the Web3 landscape, their impact on traditional financial systems becomes more pronounced, compelling institutions to adapt as well.
-
6.4 Impact on Traditional Financial Systems
The rise of Web3 and cryptocurrencies is beginning to influence traditional financial systems significantly. As DeFi platforms gain traction, banks and financial institutions are being compelled to adapt to this new landscape. Many are exploring partnerships with blockchain projects or developing their own digital currencies to remain competitive.
For instance, JP Morgan has entered the blockchain space by launching its own cryptocurrency (BBC, 2019), JPM Coin, aimed at facilitating instantaneous cross-border payments. This move highlights a growing recognition that cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can enhance efficiency and reduce costs in traditional banking operations.
Moreover, regulatory bodies are starting to take notice. As the popularity of cryptocurrencies grows, regulators are increasingly focused on creating frameworks that ensure consumer protection while fostering innovation. This regulatory evolution is crucial for the sustainable growth of the cryptocurrency market and its integration into the broader financial system.
8. Challenges and Risks
While Web3 presents numerous opportunities; it also comes with its challenges.
- Regulatory uncertainty remains a key issue, as governments across the globe are still working to establish frameworks for cryptocurrencies. The United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has increased its scrutiny of cryptocurrency projects, creating uncertainty around future regulations.
- Scalability is another major hurdle. Popular blockchains like Ethereum have faced congestion issues, leading to high transaction fees during periods of high demand. Solutions such as Layer 2 scaling technologies like Polygon and alternative blockchains like Solana are working to address these issues, but achieving full interoperability between blockchain networks remains a challenge.
- Additionally, security vulnerabilities are a significant concern. High-profile incidents like the $600 million Poly Network hack underscore the importance of security measures.
As decentralized systems grow, so do the avenues for scams, fraud, and hacking, making robust security frameworks critical. Despite these challenges, ongoing technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks are paving the way for a more secure and integrated future, where Web3.0 and traditional finance converge.
9. Future Outlook
The future of Web3 and cryptocurrencies looks promising, with innovations continuing to drive adoption and integration into traditional financial systems. JPMorgan is already utilizing blockchain for cross-border payments (Cross-Border Payment Modernization – JPMorgan), demonstrating the blend of decentralized technology with established financial institutions.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing are also expected to influence the future of Web3.0. AI could enhance smart contract automation, while quantum computing might revolutionize cryptographic security systems, creating new possibilities for blockchain technology.
Moreover, the adoption of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could serve as a bridge between government-backed and decentralized assets, further accelerating the integration of cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance.
10. Conclusion
The impact of Web3 on cryptocurrencies is not merely an upgrade to the internet or financial systems; it represents a fundamental shift in how we understand value and ownership. Cryptocurrencies lie at the heart of this transformation, reshaping the economic landscape and enabling innovative business models and investment strategies.
As we move further into this decentralized future, now is the perfect time to explore these technologies and integrate them into your business strategies. At Codora, we specialize in helping businesses leverage blockchain and Web3.0 technologies to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving financial landscape. Whether you’re looking to adopt decentralized finance solutions, implement tokenization, or develop smart contracts, our team is here to support you.
Collaborate with Codora
Reach out to us at hello@codora.io and discover how we can help you navigate the future of Web3 and cryptocurrencies. Let’s work together to bring your blockchain vision to life and lead the next wave of innovation in finance.

